European Markets
Corporate and Business News
- German investor morale fell more than expected in January. The ZEW economic research institute reported that the economic sentiment index dropped to 10.3 points from 15.7 points in December.
- German exporters expect a 2.7% drop in sales in a “bleak” 2025. This outlook is driven by several factors, including reduced orders, declining investments, and increasing insolvencies. Additionally, about 80% of businesses involved in foreign trade expect further declines in sales this year.
- German producer prices rose 0.8% year-over-year in December. This increase was primarily driven by higher prices for capital goods, non-durable consumer goods, durable consumer goods, and intermediate goods. However, energy prices actually decreased during this period.
- French factory sentiment darkens as 2025 economic clouds gather, with the manufacturing sector experiencing a notable decline. The overall business climate indicator for January 2025 is at 95, which is below the long-term average of 100.
- Investors “make Europe great again” with significant stock allocations, marking the second-largest allocation in a quarter of a century.
- Unicredit chief hopes for clarity on the planned takeover of Commerzbank by the end of 2025. CEO Andrea Orcel mentioned that discussions with the new German government will be crucial.
- According to Manager Magazin, Volkswagen plans to sell 15% of Traton shares in the first half of 2025. This sale is expected to raise approximately 2 billion euros ($2.09 billion).
- Europe accused China of unfairly blocking EU companies, particularly in sectors like renewables and electric vehicles. China has responded to the EU’s accusations by claiming that it is imposing unfair trade and investment barriers on Chinese firms through the EU’s Foreign Subsidies Regulation.
Debt and Monetary Policy News
- The European Central Bank (ECB) says it is confident inflation will stabilize at its 2% target, allowing for the possibility of rate cuts in the near future.
- The eurozone’s current account surplus narrowed in November. The surplus decreased to €27 billion, down from €30 billion in October primarily due to a reduction in surpluses for services and primary income.
- UK borrowing jumped in December as debt interest climbs. The public sector borrowed £17.8 billion, which is £10.1 billion more than in December 2023. This marks the highest December borrowing in four years.
- The Bank of England says it is open to pro-growth bank reforms. This includes simplifying post-Brexit rules for small banks and encouraging insurers to invest in British assets.
- France saw record demand for its first syndicated bond sale since its election. The sale attracted €134 billion ($138.98 billion) in orders, far exceeding the €10 billion target. This strong demand reflects investor confidence in the new government’s ability to stabilize the economy and pass a much-needed budget.
Asian Markets
Corporate and Business News
- Mitsubishi Chemical advanced the sale of its pharmaceutical unit, with Bain Capital as the leading candidate. The deal is valued at approximately $3.2 billion (500 billion yen) and is in the final stages of negotiation.
- Suntory Holdings CEO highlighted supply chain risks in US investments. He noted that while Japanese firms remain optimistic about investing in the US, they must demonstrate that their investments will create jobs and contribute positively to the US economy.
- Toyota’s Hino Motors agreed to a $1.6 billion U.S. diesel emissions settlement. The settlement includes a criminal fine of $521.76 million and a five-year probation period during which Hino will be prohibited from importing any diesel engines it has manufactured into the US.
- Nintendo revealed plans to release the Switch 2 this year. Despite the excitement, Nintendo’s shares dropped by 4% following the announcement as investors were reportedly disappointed by the lack of detailed information on the price, launch date, and software plans.
- Safran India is targeting a nearly 70% revenue boost in 2025, driven by its involvement in India’s Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission and increasing private-sector contracts.
- India’s Bharat Petroleum will invest $121 million in an Indonesian oil and gas block. This strategic move underscores its efforts to expand its international footprint and strengthen energy ties between India and Indonesia.
- Tata Motors is investing in local battery production amid rising EV competition. The company plans to spend $1.5 billion to build a battery gigafactory in India, which is expected to begin production in 2026.
- China Vanke’s CEO, Zhu Jiusheng, has reportedly been detained by authorities, deepening concerns about the company’s future and the broader property sector in China. This development comes as China Vanke, one of the country’s largest property developers, faces significant financial challenges, including a $45 billion debt burden.
- China’s crude oil imports from Russia reached record highs in 2024, increasing by 1% compared to 2023. Russia has become China’s top crude oil supplier, surpassing Saudi Arabia, whose exports to China declined by 9%.
Debt and Monetary Policy News
- The Bank of Japan has raised its key interest rate to 0.5%, the highest level in 17 years, amid persistent inflation and rising wages. The move marks a significant shift from Japan’s long-standing ultra-loose monetary policy, which aimed to combat deflation and stimulate economic growth. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projects additional rate hikes through 2025–2026.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been actively selling dollars to support the Indian rupee amid recent volatility. This intervention comes as the rupee hit an all-time low of 86.39 per U.S. dollar, driven by a surge in the dollar index and expectations that the Federal Reserve will proceed cautiously with rate cuts this year.
- The Indian housing market showed resilience in 2024 despite economic headwinds. the market saw robust growth, with over 300,000 homes sold across the top seven cities, driven by steady economic growth and infrastructure improvements. This trend is expected to continue into 2025.
- The People’s Bank of China has kept benchmark lending rates unchanged. The unchanged rates reflect the PBOC’s cautious approach amid economic uncertainties and external pressures.
- The Chinese yuan remains stable following Trump’s tariff posturing. Investors have been cautiously optimistic, as Trump’s recent comments suggested a softer stance on trade tariffs, which helped alleviate some market fears.
Latin American Markets
Corporate and Business News
- Brazil’s Azul and Gol Airlines have announced a potential merger as a survival strategy in the country’s turbulent aviation market. This merger aims to create one of the largest airlines in Latin America.
- Global airlines, including United Airlines, American Airlines, Air France-KLM, British Airways parent International Airlines Group, and Lufthansa, are in discussions with Brazil’s Gol Linhas Aéreas as part of its Chapter 11 bankruptcy exit strategy.
- Nubank’s CEO is considering relocating the company’s domicile to Britain and expanding US operations, highlighting its international ambitions.
- China halted Brazilian soy shipments from five firms over quality concerns, disrupting a critical export sector. The affected companies include Terra Roxa Comercio de Cereais, Olam Brasil, C.Vale Cooperativa Agroindustrial, Cargill Agricola SA, and ADM do Brasil.
- Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum has unveiled an ambitious economic strategy, known as the “Mexico Plan,” aimed at reducing Mexico’s reliance on Chinese imports and boosting domestic and US-sourced alternatives.
- Brazil’s JBS reached an agreement with the US Department of Labor to support individuals affected by child labor at its facilities. As part of this agreement, JBS will provide $4 million to assist individuals and communities impacted by unlawful child labor practices.
- Argentina recorded its largest trade surplus in 18 years, fueled by energy exports under President Milei’s economic reforms.
Debt and Monetary Policy News
- Economists expect Brazil’s interest rates to surpass 15%, driven by fiscal challenges and inflation trends. Inflation in Brazil has been persistently high, with the annual rate reaching 4.83% in December 2024.
- Mexico’s inflation is projected to fall below 4% in January 2025, paving the way for potential larger rate cuts by the central bank. The central bank has already implemented several rate cuts in 2024, bringing the benchmark interest rate down to 10.25%.
- Brazil’s central bank intervened in foreign exchange markets, selling $3 billion to stabilize its currency, the real, amid fiscal concerns. This intervention aims to address the significant depreciation of the real, which has been driven by market unease over Brazil’s fiscal framework and rising inflation.
- Mexican executives brace for economic stagnation following President Trump’s return, reflecting heightened policy uncertainty. A recent survey by KPMG revealed that about 60% of nearly 700 executives expect the Mexican economy to stagnate in 2025, with 24% predicting a recession.
Commodities Spotlight
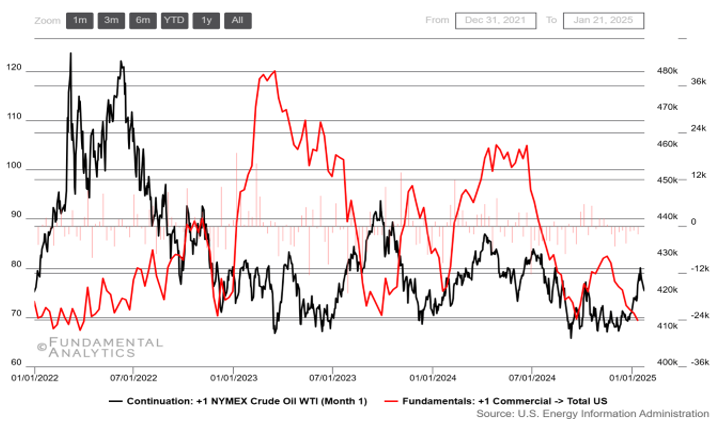
Crude Oil Tumbled on Announcement of Trump’s Energy Strategy
Source: Fundamental Analytics
WTI crude oil slipped toward $75 per barrel on Thursday as President Donald Trump delivered a virtual address at the Davos forum. In his speech, Trump announced plans to ask Saudi Arabia and OPEC to lower oil prices, emphasizing his administration’s energy priorities. He highlighted early executive actions, including declaring a national energy emergency to “unlock the liquid gold” of US oil and gas, exiting the Paris climate agreement, and ending what he called the “green new scam.” Meanwhile, the latest EIA data showed US crude inventories fell by over 1 million barrels last week, alongside a surge in fuel stockpiles, both loosely in line with market expectations.
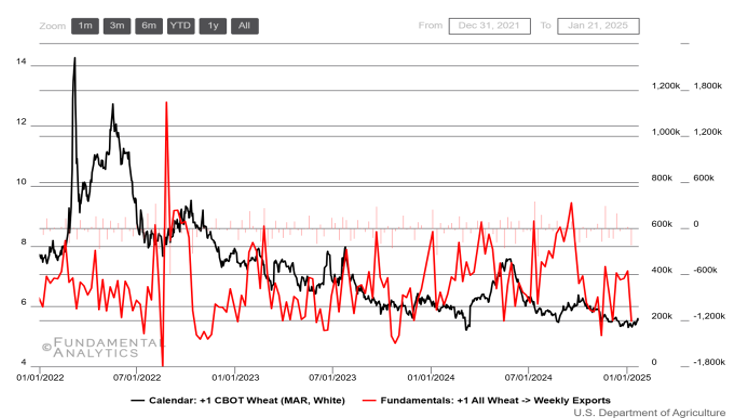
Wheat Futures Hovered Around $5.5 Mark, Amid Weather Concerns
Source: Fundamental Analytics
Wheat futures eased toward $5.50 per bushel, down from a recent one-month high of nearly $5.59 per bushel, which was driven by concerns over severe cold in some US wheat belts and persistent drought conditions in Argentina. The pullback was largely attributed to a technical correction, with traders continuing to monitor President Donald Trump’s trade policy stance. Meanwhile, the USDA’s attaché in Canberra projected Australian wheat production at 32 million metric tons, the third-highest on record, despite difficulties encountered during the growing season. The Russian wheat crop held steady this month, but weather-related risks remain a potential concern.